Events can be predictable and occur at known frequencies, such as scheduled regulatory inspections, or unpredictable, such as spills and other accidents/incidents. Although the specific time that an event occurs may not be known, the tasks to perform in response to the event are known in advance. Event Tasking is used to set up event templates for predictable and unpredictable events, establish task templates for response tasks, and associate the appropriate task templates with each event template in the order the tasks are to be completed. At this point, the task templates are not live Task Assignments; they do not appear in any Task List. When an event occurs, the appropriate event template is activated and the event's task templates become live Task Assignments as defined by the task template configuration set up for the event. Live event Task Assignments function in the same manner as routine Task Assignments. An event template can be reused as often as necessary; a separate set of Task Assignments is activated for each occurrence.
When an event template is set up, the event is categorized by an Event Type and can be associated with an entity. Otherwise, an entity is specified when the event is activated. An event template can also be designated to require approval before its tasks become live task assignments. Reviewers/approvers can be defined for each entity and event type. Reviewers are authorized to directly activate an event that requires approval, as well as approve or reject an activation proposed by a user without authorization. Establishing reviewers/approvers provides a mechanism for oversight and control of the events that are activated at your facility. An individual reviewer can be assigned to more than one event type and multiple reviewers can be associated with each event type. An option is available to extend reviewer/approver authorization to the same event type at the entity's child (including descendents) entities.
Task templates and event templates can be set up as:
Generic - (recommended) Common Task and Event templates can be re-used for various events, thereby expediting data entry and simplifying template maintenance over time. The generic option also allows standards to be set at the corporate level.
Entity-specific - Task and Event templates are set up by entity and can only be used in events activated for the entity associated with the templates.
Business Unit - Task and Event templates are set up for an entity, however, they can be used in events activated for that entity and all of its child (including descendents) entities. In this case, a user at the child entity is not required to have access to the parent entity in order to activate an event for the child entity using the parent's business unit event template.
Task templates are associated with event templates as follows:
Generic task templates can only be associated with generic event templates.
Entity-specific task templates can only be associated with entity-specific event templates established for the same entity.
Business unit task templates can only be associated with business unit event templates established for the same entity.
Since generic task templates can become live task assignments for any entity and business unit task templates can become live task assignments for multiple entities within the parent/child hierarchy, a specific contact/team cannot be designated for the Task Owner, Team, Task Initiator, Supervisor, and Supervisor Team. Contact Types and Team Types are entered instead. Then, when an event is activated for an entity, contact/team types are mapped to actual contacts/teams.
A task template can be associated with multiple event templates.
Tasks can be configured to operate in parallel (concurrently) or serially (dependently), or as a combination of both for a single event. For an event with parallel tasks only, all tasks simultaneously become active Task Assignments at the time of Event Activation. For an event with serial tasks or both serial and parallel tasks, the tasks become live Task Assignments as dependencies are met. In a series of tasks, a specific task must be completed (Task Status = Completed) before the next task is activated. The task completion requirement is the dependency. A serial or parallel task can also be set up as a Conditional task that includes a Yes/No question and requires a decision before the task can be marked completed. In this case, both the task decision and completion requirements are the dependencies. A conditional task provides the capability to configure one set of tasks to be activated when the decision is Yes, a different set for a No decision, and a different set whether the decision is Yes or No.
Task templates are assigned to an event template using a hierarchical tree format that provides a visual representation of the task work flow for the event. The task template ID, the task statement, and the following icons identify each task in the hierarchy:
|
= |
The task will become a live Task Assignment at the time of Event Activation. |
|
= |
The task will become a live Task Assignment when the parent task is completed. |
|
= |
The task will become a live Task Assignment when a Yes decision has been entered for the parent task and the parent task has been completed. |
|
= |
The task will become a live Task Assignment when a No decision has been entered for the parent task and the parent task has been completed. |
Tool tips are also available on each level of the hierarchy to help identify the task work flow.
The Event Tasks section on the Event Template form is used to establish the task configuration for an event. (Root Node is the top level for all hierarchies.) Three example task hierarchies are provided below.
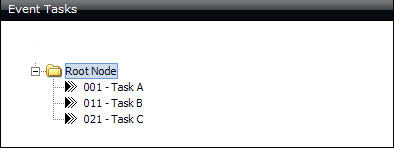
The example below shows a configuration of parallel tasks only. All of the tasks will become live task assignments simultaneously when the event is activated.
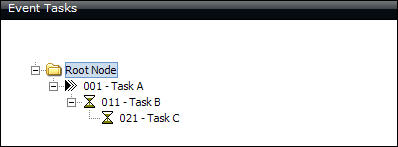
The example below shows a configuration of serial tasks. Task A is the only task that will become a live task assignment when the event is activated. Upon completion of Task A (Task Status = Completed), Task B will become a live task assignment. Upon completion of Task B, Task C will become a live task assignment.
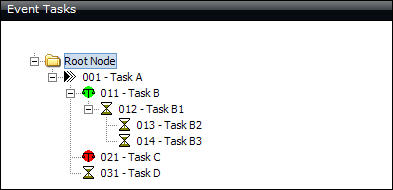
In the following example, Task A is a conditional task as evidenced by its child nodes. One set of tasks has been established for a Yes decision (Task B) and another for a No decision (Task C). Task A becomes a live task assignment when the event is activated and requires a Yes/No entry before it can be completed (Task Status = Completed).
When the decision is Yes and Task A has been completed, Task B will become a live task assignment. Upon completion of Task B, Task B1 will become a live task assignment. Upon completion of Task B1, Task B2 and Task B3 will become task assignments simultaneously. Task C will not become a live task assignment for the event.
When the decision is No and Task A has been completed, Task C will become a live task assignment. Task B, Task B1, Task B2, and Task B3 will not become live task assignments for the event.
Task D becomes a live task assignment when Task A has been completed, regardless of the Yes/No decision. Task D and either Task B or Task C will become live task assignments concurrently when Task A has been completed.
![]() Tip: It is not necessary to establish a separate path for
each decision at all times. For example, if no further action is necessary
when the decision is No, set up subsequent tasks for a Yes decision only.
Tip: It is not necessary to establish a separate path for
each decision at all times. For example, if no further action is necessary
when the decision is No, set up subsequent tasks for a Yes decision only.
Event Activation is the process of launching event tasks as live task assignments. For generic and business unit templates, an entity must be specified and all contact types and team types that were assigned to the task templates associated with the event must be mapped to actual contacts and teams.
When event templates have been designated as requiring approval before the event's tasks become live task assignments, an authorized reviewer/approver must initiate the actual activation. An unauthorized user can propose an event activation. All reviewers/approvers established for the entity and event type associated with the proposal automatically receive an email notification with links to the event activation record and the event template record. An option to approve or reject the activation is available. Upon activation/rejection an email notification is automatically sent to the user who submitted the proposal and the reviewers/approvers who received the initial proposal notification so all parties are aware of the outcome.
For historical purposes, comments, such as reasons for the activation, are required for each activation including proposed activations and rejected activation requests.
After activation, a Tasks section is displayed on the Event Activation form that lists the live task assignments associated with the event. The task due date and status are provided along with a link to the task assignment record.
Due to data interdependencies (e.g., event types and task templates must exist to set up event templates), a suggested event tasking work flow is provided below.
Ensure a valid email address has been entered for all personnel involved with event tasking (e.g., contacts, reviewers, approvers, etc.) on the Contacts and Personnel form.
Ensure contact types and team types have been set up and associated with the appropriate contacts/teams. Assign types for contacts on the Entity Contacts form and for teams on the Contact and Personnel Team form.
Ensure each contact/team associated with a contact/team type is also available for task assignments. Contacts can be granted task assignment availability on the Entity Contacts form and teams on the Contact and Personnel Team form.
Establish event types on the Event Type validation form.
Set up event type reviewers/approvers on the Event Type Reviewer form (or the Event Type form).
Establish generic, entity-specific, and/or business unit task templates.
Set up event templates and associate task templates in the appropriate completion sequence for each event.
When an event occurs, activate an event template using the Event Activation form or the Event Template form.